diff options
| author | Jack Sangdahl <[email protected]> | 2025-08-25 13:19:58 -0600 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Jack Sangdahl <[email protected]> | 2025-08-25 13:19:58 -0600 |
| commit | 98eef52499de73f369cc7e4a6e11938a1c6d3367 (patch) | |
| tree | 389bbb9017f7f2bde8c9b14bedfd795cda41e47b | |
| parent | f0a4209eaec07cd0eb8bb7ff15be34f8adb1437c (diff) | |
| download | leetcode-98eef52499de73f369cc7e4a6e11938a1c6d3367.tar.gz leetcode-98eef52499de73f369cc7e4a6e11938a1c6d3367.zip | |
chore: Improve readme
| -rw-r--r-- | readme.md | 62 |
1 files changed, 26 insertions, 36 deletions
@@ -1,12 +1,10 @@ -## leetcode -This repository contains my Leetcode solutions for [user 0x6A73](https://leetcode.com/u/0x6A73). -the daily challenge is solved in both C and Python3, but there are also -some problems solved in C++ and Rust. +## Leetcode -### notes -[`leetcode.h`](leetcode.h) contains various includes, standard leetcode -structs (`ListNode`, `TreeNode`), and some helpful macros, like -calculating the size of a C array using `builtin` functions. +This repository contains my Leetcode solutions for [user 0x6A73](https://leetcode.com/u/0x6A73). Generally, the daily challenge is solved in both C and Python3. + +### Notes + +The [`leetcode.h`](leetcode.h) header file contains various includes, standard Leetcode structs (`ListNode`, `TreeNode`), and some helpful macros, like calculating the size of a C array using `builtin` functions. ```c #define IS_ARRAY(value) \ (!__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof((value)), typeof(&(value)[0]))) @@ -14,50 +12,42 @@ calculating the size of a C array using `builtin` functions. #define ARRAY_SIZE(array) \ (__builtin_choose_expr(IS_ARRAY((array)), \ sizeof((array)) / sizeof((array)[0]), (void)0)) -// ... -int res = func(arr, ARRAY_SIZE(arr)); + +// foo.c +int arr[] = {1, 2, 3}; +int foo = func(arr, ARRAY_SIZE(arr)); ``` -[`leetcode.c`](leetcode.c) has helpful functions to fill `ListNode` and -`TreeNode` data structures with provided data, and also print data -returned by such functions. For example, see the following `main` functions. +The [`leetcode.c`](leetcode.c) file has helpful functions to fill `ListNode` and `TreeNode` data structures with provided data, and also print data returned by such functions. For examples, see the following `main` functions. -**ListNode data type** +#### `ListNode` data type  + ```c int main() { - // head = [0,3,1,0,4,5,2,0] - struct ListNode *head = listnode_create(0); - head->next = listnode_create(3); - head->next->next = listnode_create(1); - head->next->next->next = listnode_create(0); - head->next->next->next->next = listnode_create(4); - head->next->next->next->next->next = listnode_create(5); - head->next->next->next->next->next->next = listnode_create(2); - head->next->next->next->next->next->next->next = listnode_create(0); - struct ListNode *res = func(head); - listnode_print(res); + int input[] = {0, 3, 1, 0, 4, 5, 2, 0}; + struct ListNode *head = listnode_build(input, ARRAY_SIZE(input)); + listnode_print(head); } ``` -**TreeNode data type** +#### `TreeNode` data type 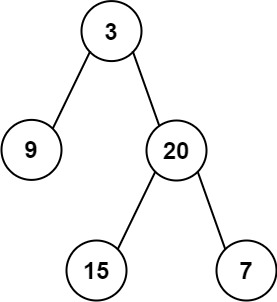 + ```c int main() { - // root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] - struct TreeNode *root = treenode_create(3); - root->left = treenode_create(9); - root->right = treenode_create(20); - root->right->left = treenode_create(15); - root->right->right = treenode_create(7); - struct TreeNode *res = func(root); - treenode_print(res); + int input[] = {3, 9, 20, -1, -1, 15, 7}; + // note: -1 denotes a 'null' leaf. if a problem's input depends on + // this value, use treenode_create() to individually create each node + struct TreeNode *root = treenode_build(input, ARRAY_SIZE(input)); + treenode_print(root); } ``` -Also functions to aid in working with 2D C arrays: +#### 2D Array Helpers + ```c int func(int **edges, int edgesSize, int *edgesColSize); @@ -65,7 +55,7 @@ int main() { // edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]] int edges_input[6][2] = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {1, 4}, {2, 5}, {2, 6}}; struct two_d_arr edges; - two_d_arr_init(&edges, 6, 2, edges_input); + two_d_arr_init(&edges, ARRAY_SIZE(edges_input), ARRAY_SIZE(edges_input[0]), edges_input); int res = func(edges.arr, edges.row_size, edges.col_size); two_d_arr_free(&edges); } |
